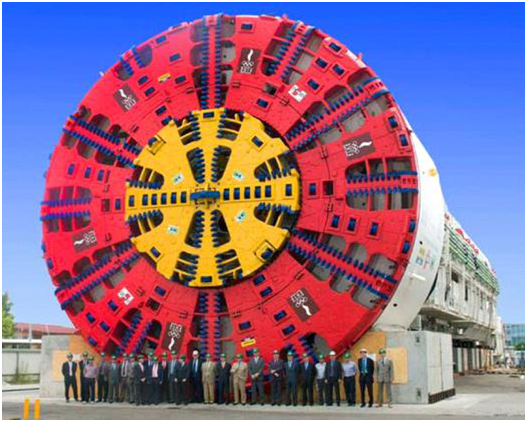

WHAT IS THE TBM?
TBM (tunnel boring machine) is the machine which use for the excavation of tunnel, galery, underground openings in metro, water, energy construction and mining projects etc.
History
TUNNEL boring was originally attempted over 150 years ago, simultaneously yet independently in England, Europe and North America. The original attempts are generally considered failures, except for the 1.5km Shakespeare tunnel in Dover, a part of the original Channel tunnel, bored over 100 years ago.
The imagination of scientists and engineers were far ahead of the technology necessary to turn their concepts into practical reality.
When we use the TBM we gain ;
Time
Money
Comfort
Operational advantages
There are a number of inherent advantages to tunnel boring which are difficult to quantify yet have a considerable impact on the outcome of excavation rates and costs. These are difficult to value in a tender. These advantages cannot fully be appreciatedexcept from firsthand tunnel boring excavation experience.
Some of these are:
• structural stability and safety at the face and work area
• continuous (non-cyclic) operation
• consistent, less skilled and easily trained operations (labour is assigned to limited tasks that are repetitive, become routine, and may even produce competition among then labourers)
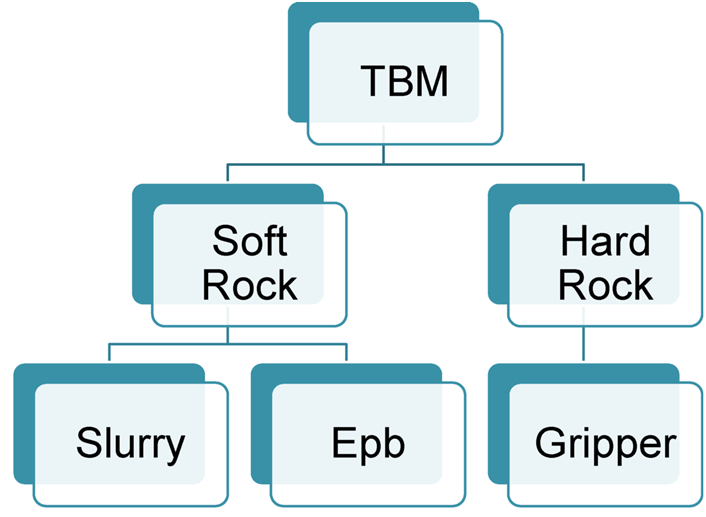
TYPES OF TBM
EPB (Earth Pressure Balance)
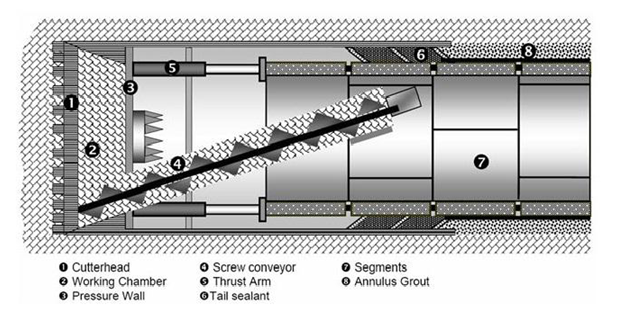
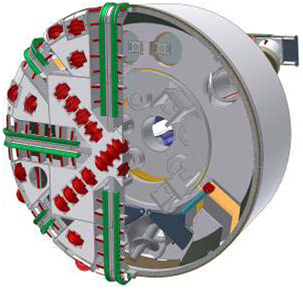
The EPB excavation mode provides continuous support to the tunnel face by balancing the earth pressure against the forward pressure of the machine. The soil excavated by the cutting head is accumulated under pressure in the cutting head chamber and is then excavated by a rotating conveyor. As the tunnel is being mined by the EPB TBM, the segmented concrete sewer liner is continuously constructed into rings within the tail shield of the machine. As the machine moves forward, the rings are grouted in place. This eliminates the need to re-visit the tunnel for secondary construction making it a one-pass system.
Working Area Condition EPB
-Silt and clay (fine grained size)
-Max 4 bar pressure (if over pressure we can’t use)
-We do not want more water
Advantages of EPB
-In case of face collapse amount of ground loss is limited
-Muck is immediately ready for disposal
-Overall simpler system to learn, operate and maintain
– In case of face collapse amount of ground loss is limited
– Able to take advantages of self-supporting grounds
– Better overall production rates are possible over SPB TBMs
– Lower capital cost
– Smaller site and launch shaft
– Lower consumption of additives (no slurry circuit)
Disadvantages of EPB
-Requires higher torque
-Requires greater Cuttinghead power
-Required confinement pressure must be calculated
-Muck is exposed into tunnel
Slurry type TBM
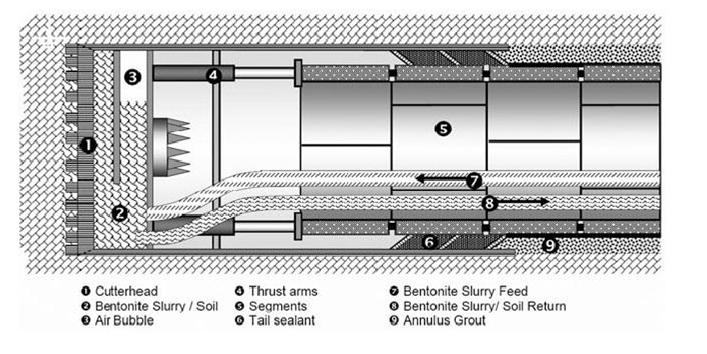
Working Area Conditions Slurry
Sand and gravel
If we got more water income (slurry condition )
We can use approxiametly more than 10 bar pressure ( i.e In Bosphorus 13 bar pressure)
Advantages of Slurry
– Required pressure is determined / controlled by system
– Lower torque
– Lower Cuttinghead Power
– Contaminated muck is not exposed until it reaches the surface
– Able to integrate rock crusher
– Cleaner Tunnel Environment
Disadvantages of Slurry
-Requires a large size job site
-Higher capital costs
-Higher power requirement
-Requires extensive addition of material

